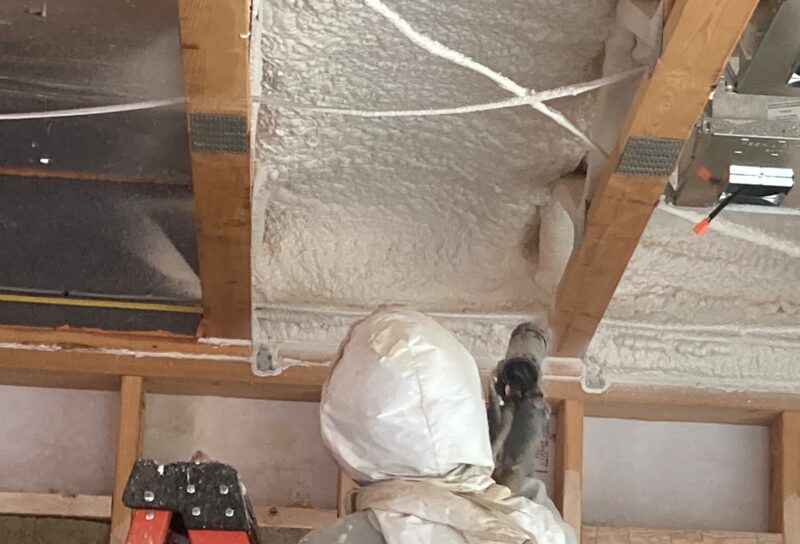
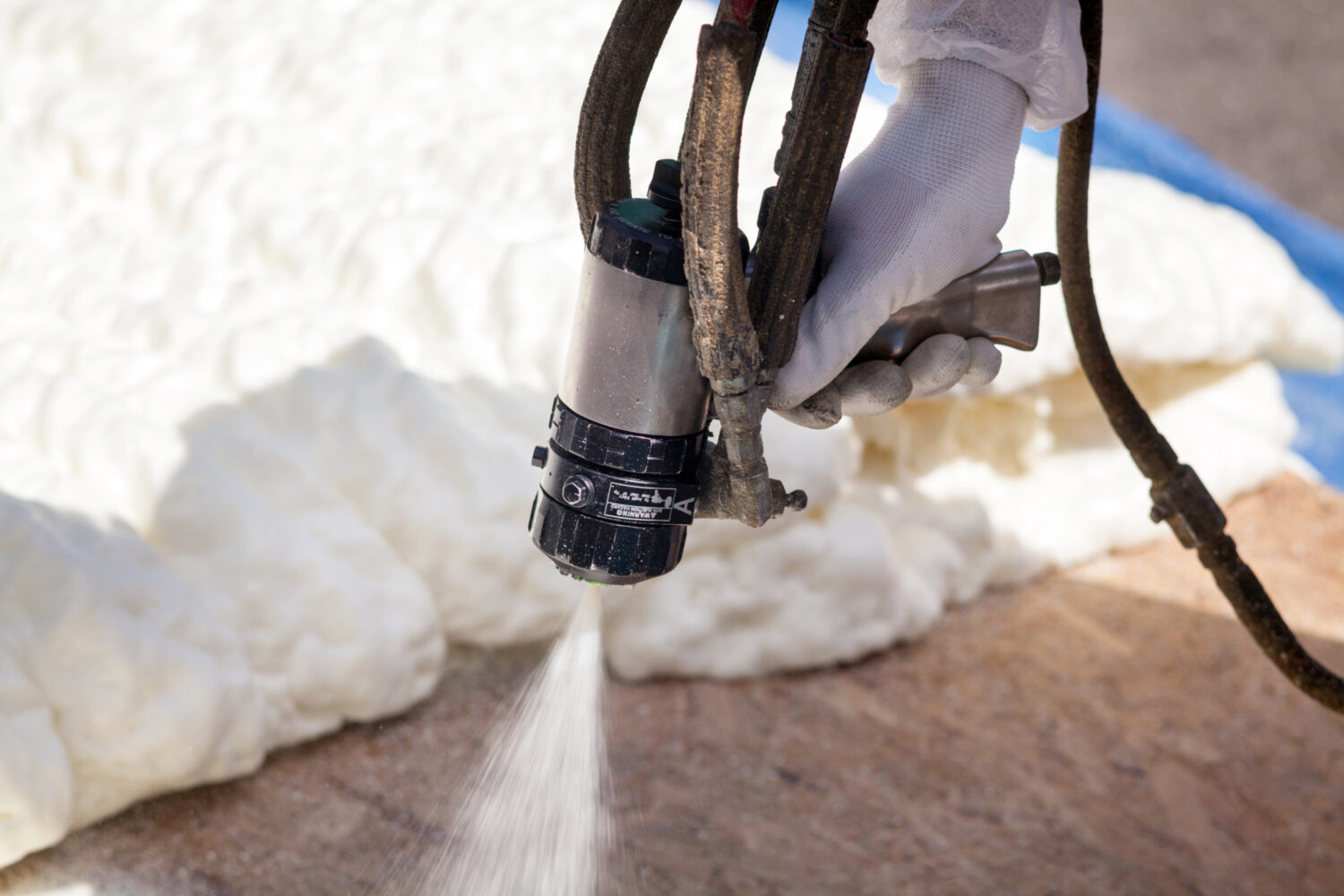
Because spray polyurethane foam is fully adhering and seals hard-to-reach penetrations, it provides unequaled air sealing properties for the entire building envelope. Reduced uncontrolled air leakage results in lower utility bills and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
BASF manufactures both closed-cell and open-cell spray polyurethane foam products for residential and commercial construction, providing the right SPF system for any type of well-engineered building envelope. The BASF two component application process features a wide range of specially formulated polyurethane spray foam offerings that meet specific site and surface requirements.
Additionally, BASF also offers a number of waterproofing or damp-proof coating materials resulting in high-performance, durable spray foam roofing systems for any climate that stand the test of time.
Due to the technical skill required, these systems must only be applied by professionally trained spray foam contractors with experience and high-quality processing equipment, specially designed for SPF applications.